The Importance of Medieval Shields
During the medieval period, shields served as crucial defensive tools for soldiers on the battlefield. They provided a means of protection against various weapons, such as swords, axes, and arrows. Shields were typically made from sturdy materials such as wood or metal and were designed to withstand the impact of enemy attacks.
Shields as a Crucial Defensive Tool
In the chaos of battle, shields were vital for protecting the body from direct blows. They were held in the hand or strapped to the arm, allowing the warrior to maneuver and block incoming strikes. The size and shape of shields varied, with different designs catering to specific combat techniques and preferences.
Shields acted as the first line of defense, intercepting blows and reducing the impact on the soldier’s body. They were especially effective in deflecting or dispersing the force of edged weapons like swords or axes. This allowed the soldier to maintain their balance and continue fighting.
Symbolism and Heraldry on Medieval Shields
Medieval shields were not only practical but also served as a canvas for symbolism and heraldry. Warriors decorated their shields with distinctive designs and emblems that represented their identity, allegiance, and achievements. This practice, known as heraldry, helped to identify soldiers on the battlefield, fostered a sense of pride and belonging, and facilitated recognition among allies.
Heraldic symbols on shields often included colors, animals, mythical creatures, and geometric shapes. The choice of colors held significance, with each color representing different qualities or virtues. For example, red symbolized courage, while blue represented loyalty. Animals and mythical creatures depicted on shields conveyed strength, bravery, or ancestral connections. Geometric shapes and patterns added aesthetic appeal and further distinguished individuals or families.
The symbolism on medieval shields not only served as a form of identification but also contributed to the morale and unity of the soldiers. It instilled a sense of purpose and identity on the battlefield, rallying comrades to fight together under a shared emblem.
Understanding the importance of medieval shields and the symbolism they carried provides us with a glimpse into the military culture and mindset of the time. Exploring the various types of medieval shields, such as round shields, wooden shields, kite shields, and metal shields, as well as their construction and materials, further deepens our understanding of medieval warfare and the role of shields in combat.
Origins of Heraldic Shields
To truly appreciate the significance of medieval heraldic shields, it is important to understand their origins. The early forms of shields and the emergence of heraldry played a crucial role in the development of these iconic symbols of medieval warfare.
Early Forms of Shields
Shields have been used throughout history as a means of protection in combat. In the early medieval period, shields were typically made of wood and were often round or oval in shape. These early shields provided basic defense against weapons such as swords, spears, and arrows.
As warfare evolved, so did the design of shields. Shield shapes began to vary, with different regions and cultures adopting their own distinctive styles. Shields became larger and more elongated, providing greater protection for the warriors who wielded them. Some of the early shield shapes included kite shields, round shields, and heater shields.
Emergence of Heraldry
The emergence of heraldry marked a significant turning point in the history of medieval shields. Heraldry is the system of designing and displaying distinctive coats of arms and symbols on shields and other armor. It originated in the 12th century and quickly gained popularity among knights and noble families.
Heraldry served a practical purpose in battle, allowing warriors to identify their allies and enemies on the chaotic battlefield. The designs on heraldic shields, known as coats of arms, were unique to each individual or family, symbolizing their lineage, achievements, and values.
The designs on heraldic shields were typically composed of various elements, including colors, animals, mythical creatures, and geometric shapes. Each element had its own symbolic meaning, allowing for a rich and intricate visual language to be developed.
Understanding the origins of heraldic shields provides a deeper appreciation for their role in medieval warfare and the culture of the time. By studying the early forms of shields and the emergence of heraldry, we gain insight into the evolution of these iconic symbols and their lasting legacy. To explore the different types of medieval shields in more detail, refer to our article on medieval shield types.
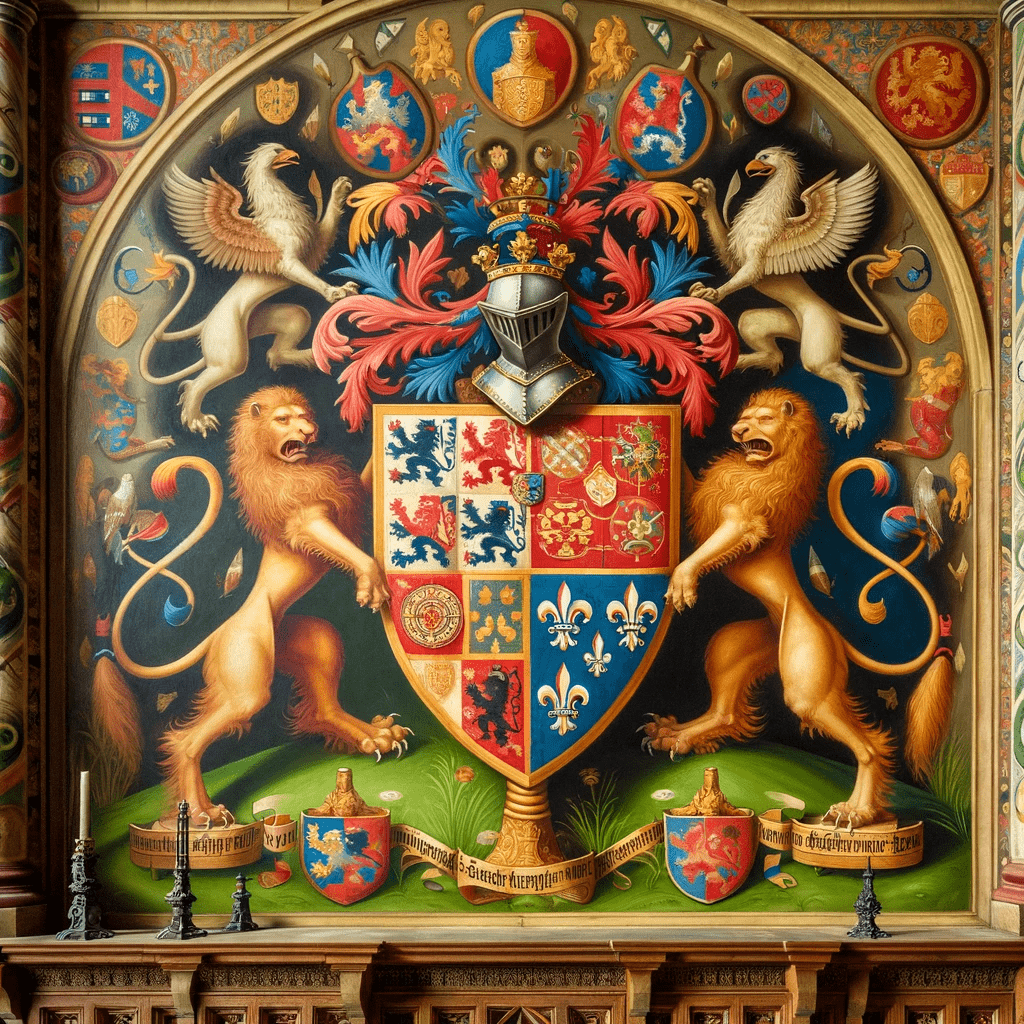
Heraldic Symbols and Meanings
Heraldic shields in the medieval era were adorned with various symbols and designs that held significant meanings. These symbols conveyed important messages about the bearer’s identity, achievements, and allegiances. Let’s explore the different elements commonly found on heraldic shields.
Colors and their Significance
Colors played a crucial role in heraldic symbolism, each carrying its own significance. Here are some of the commonly used colors and their meanings:
| Color | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Red | Valor, courage, and military strength |
| Blue | Loyalty, truth, and piety |
| Green | Hope, joy, and loyalty in love |
| Black | Grief, constancy, and wisdom |
| Gold/Yellow | Generosity, nobility, and wealth |
| Silver/White | Peace, purity, and innocence |
These colors formed the foundation of heraldic designs and were combined in various ways to create unique and personalized shields. The arrangement and combinations of colors were carefully chosen to convey specific messages about the bearer.
Animals and Mythical Creatures
Animals and mythical creatures were commonly depicted on medieval heraldic shields. These creatures held symbolic meanings and represented various qualities and attributes. Here are some examples:
- Lion: Symbol of bravery, strength, and royalty.
- Eagle: Signifies nobility, courage, and keen vision.
- Dragon: Represents power, protection, and wisdom.
- Unicorn: Symbolizes purity, virtue, and grace.
- Phoenix: Signifies rebirth, immortality, and resurrection.
These creatures were often depicted in a stylized manner, combining realistic and mythical elements. The choice of animal on a heraldic shield was a reflection of the bearer’s desired symbolism and values.
Geometric Shapes and Patterns
Geometric shapes and patterns were also prominent features on heraldic shields. These designs added visual interest and further conveyed symbolic meanings. Some commonly used shapes and patterns include:
- Cross: Symbolizes faith, honor, and protection.
- Chevron: Represents protection and military strength.
- Fleur-de-lis: Signifies purity, light, and the Holy Trinity.
- Checkered pattern: Represents bravery and constancy.
- Stripes or bars: Symbolize strength and fortitude.
These geometric shapes and patterns were often combined with animals, symbols, and colors to create intricate and visually captivating designs on heraldic shields.
Understanding the symbolism behind the colors, animals, and geometric shapes on heraldic shields provides insights into the values and aspirations of the individuals who bore them. The combination of these elements on a heraldic shield was a powerful way to communicate identity, lineage, and personal ideals. To delve deeper into the world of medieval shields, you can explore different medieval shield types and their construction materials, such as medieval wooden shields or medieval metal shields.
Types of Medieval Shields
In the medieval era, shields played a vital role in protecting warriors on the battlefield. These shields came in a variety of shapes and sizes, each with its own advantages and characteristics. Let’s explore some of the most common types of medieval shields: heater shields, kite shields, round shields, and pavise shields.
Heater Shields
The heater shield, also known as the knightly shield, was a popular choice among medieval knights. It earned its name due to its distinctive shape, resembling the outline of a heating stove. The heater shield featured a curved top and a pointed bottom, allowing it to cover the body effectively. Its design provided protection for the wielder’s torso and legs.
Kite Shields
The kite shield, as its name suggests, resembled the shape of a kite. This shield was larger than the heater shield and provided excellent coverage for the knight. The elongated shape allowed for better protection of the legs and provided ample space for displaying heraldic designs. Kite shields were commonly used by knights and cavalry during the medieval period.
Round Shields
The round shield, also known as the buckler, was one of the most ancient types of shields. It had a circular shape and was typically smaller in size compared to other shields. The round shield was lightweight and versatile, allowing for quick maneuverability in combat. It was commonly used by infantry soldiers and provided reliable defense against close-range attacks.
Pavise Shields
The pavise shield was a unique type of shield that served a different purpose compared to others. It was a large, rectangular shield that originated from Italy. Unlike the other shields mentioned, the pavise shield was not held in hand during combat. Instead, it was placed on the ground and used as a protective barrier for archers or crossbowmen. This shield provided cover while the archers took aim, allowing them to release arrows without being exposed to enemy fire.
| Shield Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Heater Shields | Curved top, pointed bottom, torso and leg protection |
| Kite Shields | Resembles a kite shape, large size, excellent coverage |
| Round Shields | Circular shape, lightweight, used by infantry |
| Pavise Shields | Rectangular shape, placed on the ground, used by archers |
Understanding the different types of medieval shields provides insight into the diverse tactics and strategies employed during battles. Each shield had its own advantages and was suited to different combat scenarios. Visit our article on medieval shield types to learn more about the fascinating world of medieval shields.
Construction and Materials
When it comes to the construction of medieval heraldic shields, two key elements deserve attention: wood and metal shield frames and coverings and reinforcements.
Wood and Metal Shield Frames
The frame of a medieval heraldic shield played a crucial role in its structural integrity. These frames were typically constructed using strong and durable materials such as wood or metal.
Wooden shield frames were commonly used due to their availability and ease of shaping. Shields made from wood were often lightweight, making them easier to maneuver in battle. Different types of wood were utilized, including oak, pine, and ash, depending on availability and the intended use of the shield. Wooden shields were typically constructed by layering thin wooden planks and bonding them together with glue or iron nails.
Metal shield frames were less common but offered superior durability and protection. Shields constructed with metal frames provided increased defense against enemy attacks. Iron, steel, or a combination of both were used to create the frames. Metal shield frames were often reinforced with additional metal strips or bands to enhance their strength and resilience.
Coverings and Reinforcements
To protect the frame and enhance the shield’s defensive capabilities, coverings and reinforcements were added to the shield.
The most common covering material for medieval shields was leather. Leather coverings provided flexibility, durability, and some resistance to arrows and slashing attacks. The leather was often treated with oils or wax to improve its resistance to moisture and extend its lifespan.
In addition to the leather covering, shields were reinforced with metal fittings such as shield bosses and rim bindings. A shield boss was a metal protrusion placed in the center of the shield to deflect direct blows and reinforce the shield’s structure. It also served as a grip for the shield hand. Rim bindings consisted of metal bands that ran along the outer edge of the shield, reinforcing it and preventing the wood or leather from splitting or fraying.
The combination of a sturdy frame, a protective covering, and reinforcements made medieval heraldic shields formidable defensive tools on the battlefield.
To learn more about specific types of medieval shields, such as round shields, kite shields, and others, visit our article on medieval shield types. For information on materials used in specific shield types, such as wooden shields or metal shields, refer to our articles on medieval wooden shields and medieval metal shields, respectively.
Heraldic Shields in Battle
When it comes to the battlefield, heraldic shields played a significant role in medieval warfare. These shields were not only defensive tools but also served tactical and strategic purposes, while also aiding in identification on the chaotic battlefield.
Tactics and Strategies
In the heat of battle, tactics and strategies were crucial for gaining the upper hand. Shields were an integral part of these tactics, providing protection to warriors as they engaged in combat. A well-crafted heraldic shield could deflect blows from swords, axes, and other weapons, reducing the risk of injury or death.
One common tactic employed with shields was the shield wall formation. This formation involved warriors interlocking their shields to create a solid barrier, forming an impenetrable wall of defense. The shield wall was highly effective in stopping enemy charges and protecting troops behind it. The shields’ design and construction played a vital role in the success of this tactic.
Another strategy involving heraldic shields was the use of shield symbols for coordination and communication on the battlefield. Knights and warriors would often bear their own unique heraldic symbols on their shields, allowing commanders to easily identify their troops amidst the chaos of battle. This facilitated better coordination and ensured troops stayed organized during the turmoil of combat.
Role of Heraldry in Identification
Heraldry, the system of designing and displaying coat of arms, was deeply intertwined with medieval warfare. Shields played a central role in displaying these heraldic symbols, aiding in identification and recognition on the battlefield. The symbols on a knight’s shield could indicate their family lineage, allegiance, achievements, or even aspirations.
By observing the symbols on the shields, commanders could quickly identify their own troops and allies, preventing friendly fire incidents and enhancing coordination. Additionally, the sight of a knight bearing a prestigious coat of arms on their shield could inspire fear in their enemies and boost the morale of their own comrades.
The use of heraldic symbols on shields extended beyond mere identification. They served as a statement of honor, valor, and lineage. Knights would proudly display their heraldry, representing their family’s history and their own prowess in battle. This visual representation of identity and lineage added a layer of complexity and significance to the presence of heraldic shields on the battlefield.
As we explore the fascinating world of medieval heraldic shields, it becomes evident that they were not just tools of defense but also strategic assets. Shields played an integral role in the tactical maneuvers and coordination of troops, while heraldry on shields aided in identification and inspired awe on the battlefield. To learn more about the different types of medieval shields, check out our article on medieval shield types.
Legacy of Medieval Heraldic Shields
The influence of medieval heraldic shields extends far beyond the Middle Ages, leaving a lasting legacy that can still be seen today. Let’s explore two significant aspects of this legacy: influence on modern heraldry and the collecting and displaying of heraldic shields.
Influence on Modern Heraldry
Medieval heraldic shields laid the foundation for the development of modern heraldry. The distinctive symbols and colors displayed on medieval shields served as a means of identification and communication on the battlefield. Over time, these symbols evolved into the intricate coats of arms that we associate with heraldry today.
In modern heraldry, the principles and traditions established by medieval shields continue to guide the design and interpretation of coats of arms. The use of colors and their significance remains an essential element, with each color carrying symbolic meaning. For example, red represents courage and strength, while blue symbolizes loyalty and truth. The animals, mythical creatures, and geometric shapes found on medieval shields continue to be prevalent in modern heraldic designs.
By studying medieval heraldic shields, you can gain a deeper understanding of the rich symbolism and history that underpins modern heraldry. For more information on medieval shield types and their influence on modern heraldry, visit our article on medieval shield types.
Collecting and Displaying Heraldic Shields
The allure of medieval heraldic shields has captured the imagination of many enthusiasts, leading to the collecting and displaying of these historical artifacts. Collectors value heraldic shields for their aesthetic appeal, historical significance, and the stories they tell about the individuals and families they represent.
Authentic medieval heraldic shields are highly sought after but can be challenging to acquire due to their rarity. However, replicas and reproductions allow collectors to own a piece of medieval history. These replicas are meticulously crafted to replicate the intricate designs and construction of the original shields.
When displaying heraldic shields, it is important to consider their preservation and presentation. Proper mounting and framing techniques ensure that the shields are protected and showcased in an elegant manner. Collectors often create dedicated display spaces in their homes, museums, or historical exhibitions to showcase their heraldic shield collections.
The collecting and displaying of heraldic shields not only allows individuals to appreciate the artistry and craftsmanship of these medieval artifacts but also serves as a tangible connection to the past. For more information on specific types of medieval shields and their characteristics, visit our articles on medieval round shields, medieval wooden shields, medieval kite shields, and medieval metal shields.
The legacy of medieval heraldic shields continues to captivate and inspire, reminding us of the rich history and traditions of the Middle Ages. Whether through their influence on modern heraldry or as cherished collectibles, heraldic shields serve as tangible reminders of the valor, honor, and identity of those who carried them into battle.
