Welcome to the fascinating world of medieval swords! In this section, we will introduce you to the enchanting realm of these iconic weapons and explore their significance in medieval warfare.
Introduction to Medieval Swords
Medieval swords were more than just tools of combat; they were symbols of power, prestige, and chivalry. These weapons played a pivotal role in shaping the medieval era and are still celebrated in modern times for their elegance and craftsmanship.
Medieval swords were primarily used by knights and warriors during the medieval period, which spanned from the 5th to the 15th century. These swords were carefully crafted with precision and skill, reflecting the artistry of the blacksmiths who forged them. They were designed to be versatile, deadly, and effective in battle, making them a valuable asset on the battlefield.
Importance of Swords in Medieval Warfare
In medieval warfare, swords were highly prized for their versatility and close-quarters combat capabilities. They were the weapon of choice for knights, who were the elite warriors of the time. The sword’s ability to deliver swift and precise strikes made it an invaluable tool in the chaos of battle.
Swords were not only used for offensive purposes but also served as a means of defense. Their length and maneuverability allowed knights to parry and block incoming attacks, providing a crucial line of defense against their adversaries. The versatility of swords made them suitable for a variety of combat situations, whether it was fighting on foot or horseback.
The importance of swords in medieval warfare cannot be overstated. They were not only weapons but also symbols of honor and social status. Owning a well-crafted sword was a mark of a knight’s prowess and served as a testament to their valor and dedication to the code of chivalry.
To delve further into the captivating world of medieval weaponry, explore our articles on medieval weapons and medieval armor. By understanding the historical context and significance of medieval swords, you can gain a deeper appreciation for these magnificent weapons that etched their place in history.
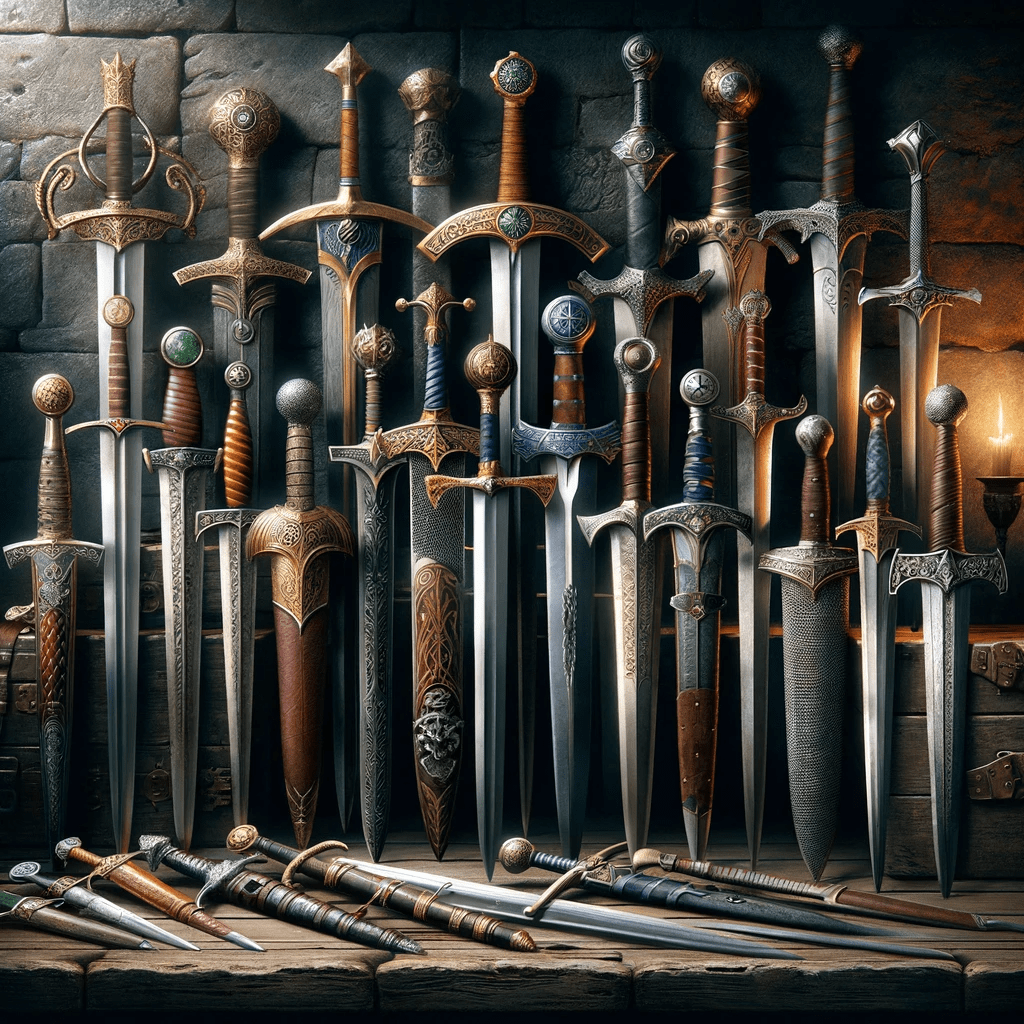

Types of Medieval Swords
When exploring the world of medieval swords, it’s fascinating to delve into the various types that were used during this era. Each type of sword had its own unique characteristics and was designed for specific purposes. Let’s take a closer look at four prominent types of medieval swords: arming swords, longswords, broadswords, and greatswords.
Arming Swords
Arming swords, also known as knightly swords or single-handed swords, were one of the most commonly used swords in medieval warfare. These swords featured a straight double-edged blade, typically measuring around 28 to 32 inches in length. The arming sword was versatile, allowing for effective slashing and thrusting maneuvers. Its design made it suitable for use with a shield or in combination with a secondary weapon.
Longswords
The longsword, also referred to as a hand-and-a-half sword, was a versatile weapon that gained popularity during the late medieval period. As the name suggests, these swords were longer than arming swords, with blade lengths ranging from 35 to 47 inches. Longswords featured a straight blade and a longer grip, allowing for two-handed use. This provided the wielder with increased control and the ability to deliver powerful, precise strikes.
Broadswords
Broadswords, also known as basket-hilted swords, were characterized by their distinctive hand protection in the form of a large basket-shaped guard. These swords were designed for both cut-and-thrust techniques, making them suitable for both offense and defense. Broadswords typically had a blade length ranging from 32 to 40 inches. The basket hilt offered excellent hand protection, making it a favored choice among knights and nobles.
Greatswords
Greatswords, as the name suggests, were the largest and heaviest of the medieval swords. These formidable weapons were primarily used by skilled and strong warriors due to their size and weight. Greatswords typically had a blade length of around 50 to 72 inches, making them capable of delivering devastating cutting blows. Due to their size, greatswords were often wielded with two hands to maximize control and power.
To truly understand the intricacies of medieval swords, it’s important to explore their anatomy, materials, and fighting techniques. By delving into these aspects, we can appreciate the significance and impact of these weapons during medieval times. For more information on medieval weapons, including swords, armor, and other weaponry, check out our comprehensive guide on medieval weapons.
Anatomy of a Medieval Sword
To truly appreciate the craftsmanship and design of medieval swords, it is important to understand their key components. A medieval sword consists of three main parts: the blade, the hilt and grip, and the pommel and crossguard.
Blade
The blade is the most prominent and functional part of a medieval sword. It extends from the hilt to the tip and is responsible for delivering strikes. Medieval sword blades are typically made of steel or iron and vary in length, width, and shape depending on the specific type of sword. The design of the blade greatly influences its effectiveness in combat.
Some common blade shapes include:
- Straight: Straight blades are versatile and effective for both cutting and thrusting. They excel at delivering precise strikes.
- Curved: Curved blades are known for their slashing abilities. The curve allows for more effective cuts and can increase the force of impact.
- Tapered: Tapered blades are wider near the hilt and gradually narrow towards the tip. This design provides a balance of cutting power and thrusting capabilities.
Hilt and Grip
The hilt and grip of a medieval sword provide the wielder with control and stability during combat. It is the part of the sword that the wielder holds onto. The hilt is typically made of materials such as wood, bone, or metal, and is designed to protect the wielder’s hand from enemy strikes.
The grip, often covered in leather or other materials for better traction, allows for a secure hold on the sword. It is important for the grip to be comfortable and provide a firm grasp to prevent the sword from slipping during battle.
Pommel and Crossguard
The pommel and crossguard are located at the opposite end of the blade from the hilt. The pommel serves as a counterweight to the blade, helping to balance the sword and improve maneuverability. It also acts as a protective knob at the end of the hilt, preventing the hand from slipping off the grip.
The crossguard, also known as the quillon, is a horizontal bar that extends from the hilt, perpendicular to the blade. Its primary purpose is to protect the wielder’s hand from an opponent’s weapon during a parry or block. The shape and design of the crossguard can vary, with some swords featuring elaborate and decorative forms.
Understanding the anatomy of a medieval sword allows you to appreciate the intricate details and functional aspects of these weapons. The combination of the blade, hilt and grip, and pommel and crossguard work together to create a formidable tool of warfare. To explore more about medieval weapons, visit our article on medieval weapons.
Materials and Construction
When it comes to the materials and construction of medieval swords, there are several key aspects to consider. Understanding these elements can provide insight into the craftsmanship and durability of these iconic weapons. Let’s take a closer look at steel and iron, forging techniques, and the sword making process.
Steel and Iron
Medieval swords were primarily crafted from a combination of steel and iron. Steel, a stronger and more durable material, was often used for the blade, while iron was used for other components such as the hilt and crossguard. The quality of the steel played a crucial role in the overall performance and longevity of the sword.
Different types of steel were used during the medieval period, including carbon steel and pattern-welded steel. Carbon steel, known for its hardness and ability to hold an edge, was a popular choice for sword blades. Pattern-welded steel, also known as Damascus steel, was created by layering and folding different types of steel together, resulting in a distinctive pattern and enhanced strength.
Forging Techniques
The art of forging played a significant role in the construction of medieval swords. Skilled blacksmiths employed various techniques to shape and strengthen the metal. One such technique was heat treatment, which involved heating the steel and then rapidly cooling it to enhance its hardness and durability. This process, known as quenching, helped to create a strong and resilient blade.
Another important technique was tempering, which involved reheating the blade to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly. Tempering helped to reduce the brittleness of the steel, making it less prone to breakage during combat. The combination of heat treatment and tempering allowed blacksmiths to create swords that were both strong and flexible.
Sword Making Process
Crafting a medieval sword was a labor-intensive process that required great skill and attention to detail. The sword making process typically involved the following steps:
- Design and Planning: The blacksmith would begin by creating a blueprint or template for the sword, taking into account the desired shape, size, and proportions.
- Material Preparation: The appropriate steel and iron would be selected and prepared for forging. This involved heating the metal to make it malleable and removing any impurities.
- Forging: The blacksmith would use a combination of heating, hammering, and shaping techniques to form the blade, hilt, and other components of the sword.
- Heat Treatment and Tempering: Once the sword had been shaped, it would undergo heat treatment and tempering to enhance its strength and durability.
- Finishing and Polishing: The sword would then be polished and refined to create a smooth and aesthetically pleasing surface. This process involved grinding, sanding, and buffing the blade and other parts of the sword.
- Hilt and Handle Assembly: The hilt, including the grip, crossguard, and pommel, would be carefully crafted and attached to the blade.
- Final Touches: The sword would undergo any final embellishments or engravings, adding to its beauty and individuality.
By understanding the materials used, the forging techniques employed, and the intricate sword making process, we gain a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship that went into creating medieval swords. These weapons continue to captivate us with their historical significance and enduring legacy. If you’re interested in learning more about medieval weapons, be sure to explore our articles on medieval weapons and medieval armor.
Sword Fighting Techniques
To fully appreciate the art of sword fighting during medieval times, it’s important to understand the various grips, stances, offensive moves, and defensive techniques employed by warriors of that era.
Grips and Stances
Mastering the proper grip and stance is crucial for effective sword fighting. There were several common grips used by medieval swordsmen, including the hammer grip and the thumb grip. The hammer grip involves firmly gripping the sword with the hand wrapped around the hilt, while the thumb grip involves placing the thumb along the back of the hilt for added control.
In terms of stances, medieval swordsmen utilized different positions depending on their preferred style of combat. Some popular stances included the guardant stance, where the fighter stands with the sword held diagonally in front of their body, and the tail guard stance, where the sword is held low and behind the body. These stances allowed warriors to maintain balance and maneuverability while engaging in combat.
Offensive Moves
Medieval sword fighting encompassed a wide array of offensive moves designed to overpower opponents. These moves often combined footwork, body positioning, and precise strikes. Some common offensive techniques included:
- Thrust: A quick, forward movement of the sword aimed at piercing the opponent’s defenses.
- Slash: A sweeping motion of the sword intended to cut or slice the opponent.
- Draw Cut: A technique involving drawing the sword across the target to inflict a deep cut.
- Hewing: A powerful swinging motion aimed at cleaving through an opponent’s defenses.
Each offensive move required exceptional timing, accuracy, and the ability to anticipate the opponent’s actions. Swordsmen trained extensively to develop these skills and execute their attacks with precision.
Defensive Techniques
In sword fighting, defense was just as important as offense. Medieval swordsmen employed various techniques to protect themselves from incoming attacks. These defensive techniques included:
- Parry: Using the sword to deflect or redirect the opponent’s strike away from the body.
- Block: Positioning the sword to intercept and stop an incoming attack.
- Dodge: Evading an attack by quickly moving out of the opponent’s striking range.
- Counterattack: Responding to an opponent’s attack with a swift and calculated strike.
Timing and anticipation were critical in executing effective defensive techniques. A skilled swordsman would read their opponent’s movements, react accordingly, and exploit any opening to launch a counterattack.
By mastering the grips, stances, offensive moves, and defensive techniques of medieval sword fighting, warriors were able to engage in intense duels and battles. These combat skills were honed through rigorous training and experience, making swordsmanship an essential aspect of medieval warfare.
The legacy of medieval sword fighting continues to captivate our imaginations and influence popular culture. To learn more about other fascinating aspects of medieval times, check out our articles on medieval weapons and medieval knights.
Legacy of Medieval Swords
Medieval swords hold a significant place in history and continue to captivate the imagination with their symbolism and status. Let’s explore the profound impact these weapons have had on modern culture, as well as the importance of collecting and preserving them.
Symbolism and Status
In medieval times, swords were more than just weapons. They represented power, honor, and social standing. Possessing a sword was a sign of nobility and a symbol of authority. Knights and nobles would often commission finely crafted swords to reflect their prestige and lineage. The design, embellishments, and materials used in the construction of these swords were carefully chosen to convey a sense of grandeur and importance.
The sword also held a symbolic value on the battlefield. It became a personal extension of a warrior’s identity, representing their skill, courage, and loyalty. The sight of a gleaming sword in the hands of a knight would inspire both fear and admiration among their foes and allies alike. The legacy of these symbols of power has left an indelible mark on our perception of the Middle Ages.
Influence on Modern Culture
The legacy of medieval swords extends far beyond their historical significance. They have become iconic symbols in literature, art, and popular culture. Countless tales of chivalry, heroism, and epic battles have been inspired by the romance and intrigue surrounding medieval swords. From the legendary Excalibur to the iconic swords wielded by fictional knights, these weapons continue to capture our imagination.
Medieval swords have also had a profound impact on the world of entertainment. Movies, television shows, and video games often feature medieval settings with characters brandishing swords as they engage in epic duels. The enduring popularity of medieval-inspired fantasy genres further highlights the lasting influence of these weapons on modern culture.
Collecting and Preserving Medieval Swords
For enthusiasts and collectors, the allure of owning a medieval sword lies in the connection to history and the craftsmanship involved in their creation. Collecting these weapons allows individuals to appreciate the artistry and technical skills of medieval blacksmiths. However, due to their rarity and historical significance, authentic medieval swords can be difficult to acquire and require careful preservation.
When collecting medieval swords, it’s important to ensure their authenticity and provenance. Expert guidance and reputable dealers can help in identifying genuine swords and verifying their historical background. Proper storage and maintenance are essential to preserve the integrity of these artifacts. Display cases, controlled environments, and regular cleaning are some of the measures taken to safeguard these valuable pieces of history.
By collecting and preserving medieval swords, enthusiasts contribute to the preservation of our heritage and enable future generations to appreciate the artistry and historical significance of these remarkable weapons.
The legacy of medieval swords continues to fascinate us, from the symbolism and status they represented in the past to their enduring influence on modern culture. Through their timeless allure, these weapons serve as a testament to the valor and honor of the knights and warriors of the Middle Ages.
