Journey into the Medieval Times
Welcome to the captivating world of medieval times, where knights, castles, and epic battles were part of everyday life. The medieval era continues to fascinate and inspire us, transporting us to a time of chivalry, bravery, and honor. Let’s explore why the medieval times hold such a special place in our hearts and delve into the importance of shields in medieval warfare.
Why Medieval Times Fascinate You
The medieval period has a certain allure that captivates your imagination. It’s a time of grandeur and adventure, where knights clad in shining armor fought for honor and glory. The tales of medieval quests, courtly love, and the code of chivalry have been passed down through generations, fueling our fascination with this extraordinary era.
The medieval times offer a glimpse into a world vastly different from our own, where life was centered around castles, feudal systems, and the pursuit of power. This period represents a unique blend of history, mythology, and fantasy, intertwining real events with legends and folklore. The rich tapestry of medieval culture, from its art and architecture to its literature and music, continues to inspire artists, writers, and enthusiasts to this day.
The Importance of Shields in Medieval Warfare
In the realm of medieval warfare, shields played a vital role in protecting warriors and influencing the outcome of battles. These wooden shields were more than just defensive tools; they were symbols of status, identity, and honor. Shields were often emblazoned with colorful heraldic designs, reflecting the knight’s lineage and allegiances.
Medieval shields were designed to withstand the rigors of combat, providing a crucial barrier between the knight and his adversaries. They were crafted with care, using sturdy wood and reinforced with metal rims or bosses to enhance their durability. Shields varied in shape and size, each type serving a specific purpose on the battlefield.
To learn more about the different types of medieval shields, check out our article on medieval shield types. It explores the fascinating world of round shields, kite shields, metal shields, and more.
The shield was not only a defensive tool but also a tactical asset. It allowed knights to form a protective wall, creating a shield wall formation that provided cover for their comrades. Shields were also used to deflect incoming blows, parry attacks, and even push back opponents.
In the chaos of battle, shields offered a sense of security and stability. They could turn the tide of a skirmish, giving knights the confidence to press forward and strike fear into the hearts of their enemies. The skillful use of shields often determined the outcome of a duel or a larger-scale conflict.
As we dive deeper into the evolution and importance of medieval wooden shields, we’ll explore the various types, characteristics, and tactical applications of these remarkable pieces of armor. So join us on this journey through time and discover the fascinating world of medieval warfare and the indomitable spirit of the knights who wielded these iconic shields.
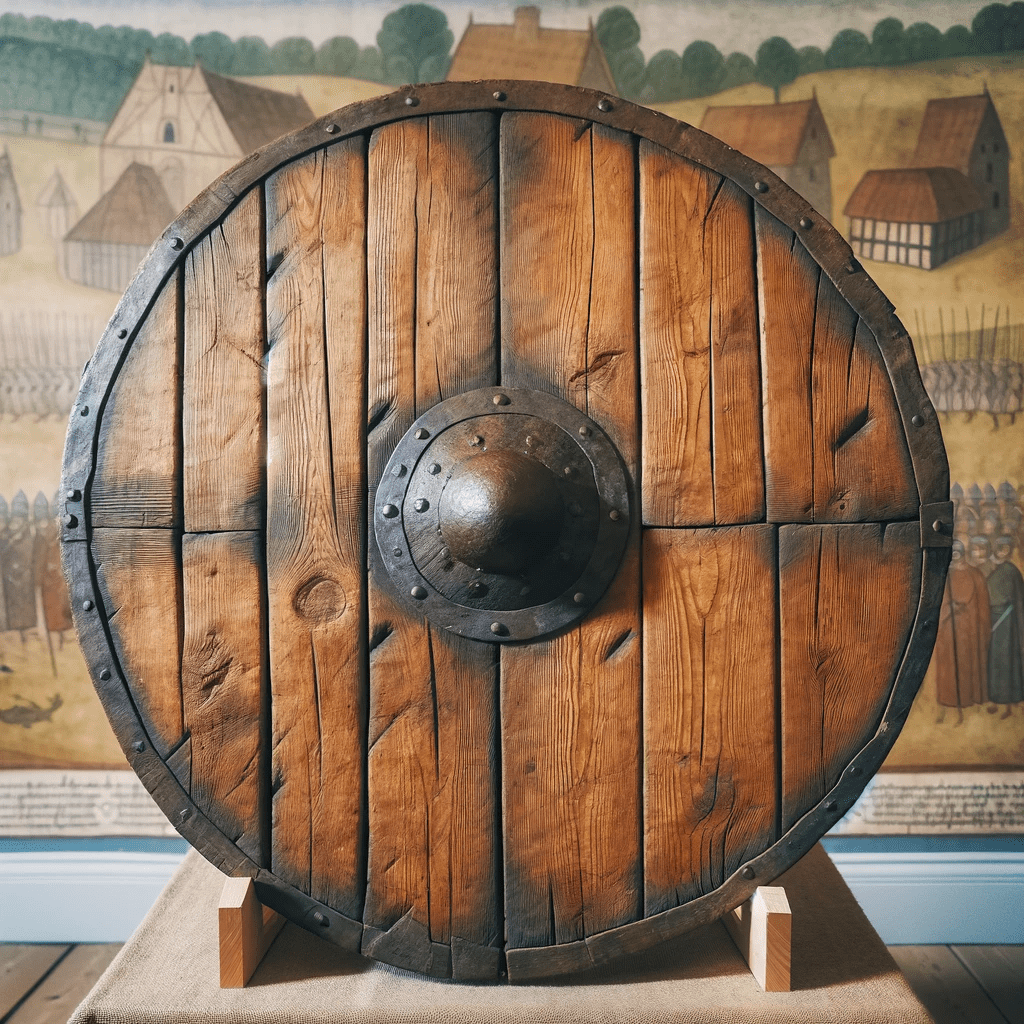
The Evolution of Medieval Shields
During the medieval era, shields played a crucial role in warfare, providing protection and defense to soldiers on the battlefield. Over time, shields evolved in design and construction, adapting to the changing needs of medieval warriors. Let’s delve into the early shield designs and the advancements in shield construction that occurred during this period.
Early Shield Designs
In the early stages of the medieval era, shields were typically made of wood, as it was readily available and easy to work with. These early shield designs were relatively simple, often featuring a round or oval shape. The wooden shields were reinforced with layers of animal hide, such as leather or rawhide, to provide additional strength and rigidity. These shields were lightweight and maneuverable, allowing soldiers to wield them effectively in combat.
Advancements in Shield Construction
As warfare techniques and weaponry evolved, so did the design and construction of medieval shields. One significant advancement was the introduction of metal reinforcements and fittings to enhance the durability and protective capabilities of the shields. Metal bosses, which were domed metal plates, were added to the center of the shields to deflect blows and reinforce the structure. These metal fittings not only strengthened the shields but also contributed to their aesthetic appeal.
Additionally, shield shapes evolved to accommodate different combat strategies. The heater shield, also known as the kite shield, emerged during the 12th century. This shield featured a distinctive triangular shape, tapering down to a point at the bottom. The kite shield provided greater protection for the lower body and legs, making it popular among mounted knights. To learn more about medieval kite shields, check out our article on medieval kite shields.
Another type of shield that gained popularity during the medieval era was the buckler shield. The buckler shield was smaller in size compared to other shields, allowing for increased maneuverability and versatility in combat. It was typically held in the off-hand, providing protection while the other hand wielded a weapon. The compact nature of the buckler shield made it suitable for close-quarters combat and fencing techniques.
As shields became more than just a defensive tool, they also started to reflect the identity and heraldry of the warriors who wielded them. Heraldic designs, such as coat of arms and symbols, were painted or emblazoned on shields to signify allegiance, rank, and family heritage. To explore more about the heraldic aspect of shields, visit our article on medieval heraldic shields.
The evolution of medieval shields showcased the ingenuity and adaptability of medieval warriors. From the simple early shield designs to the advancements in construction techniques, shields became an integral part of medieval warfare. The combination of wood and metal, along with the incorporation of heraldic elements, transformed shields into both functional and symbolic tools on the battlefield.
Different Types of Medieval Wooden Shields
In the medieval era, wooden shields played a vital role in protecting warriors on the battlefield. These shields came in various shapes and sizes, each with its own unique features and advantages. Let’s explore some of the different types of medieval wooden shields:
Heater Shield
The heater shield was one of the most popular types of medieval shields. It derived its name from its distinctive shape resembling a flat-topped heat furnace. The heater shield offered excellent protection to the wielder, covering a significant portion of their body. Its design allowed for effective blocking and deflecting of enemy attacks.
Kite Shield
The kite shield was another commonly used wooden shield during medieval times. Its elongated and tapering shape resembled the outline of a kite, hence the name. The kite shield provided ample coverage for the warrior, extending from the shoulders to the lower legs. This design allowed for greater defense while still offering maneuverability on the battlefield.
Buckler Shield
The buckler shield was a small, round wooden shield that warriors could easily carry in one hand. Its compact size and lightweight nature made it highly versatile during combat. The buckler shield was primarily used for parrying and deflecting enemy strikes, allowing the wielder to swiftly counterattack.
Pavise Shield
The pavise shield was a large wooden shield that was not held by hand but rather propped on the ground or mounted on a stand. It served as a protective barrier for archers and crossbowmen on the battlefield. The pavise shield provided cover for the archers, allowing them to reload their weapons safely.
| Shield Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Heater Shield | Resembles a flat-topped heat furnace, offers excellent protection. |
| Kite Shield | Elongated and tapering shape, provides good defense and maneuverability. |
| Buckler Shield | Small, round shield held in one hand, ideal for quick parrying. |
| Pavise Shield | Large shield propped on the ground or mounted, used for protection and cover. |
The different types of medieval wooden shields served specific purposes and catered to the needs of warriors during combat. Each shield had its own advantages, whether it was the broad coverage of the heater shield, the maneuverability of the kite shield, the agility of the buckler shield, or the protective function of the pavise shield. To learn more about medieval shield types, visit our article on medieval shield types.
These shields not only provided protection and defense but also held symbolic significance and represented the identity of the wielder. The choice of shield often reflected the warrior’s social status, allegiance, or personal preferences. Additionally, the tactical use of these shields on the battlefield played a crucial role in determining the outcome of conflicts.
By understanding the different types of medieval wooden shields, you can gain insight into the fascinating world of medieval warfare and the essential role that shields played in protecting warriors during battles.
Characteristics of Wooden Shields
Wooden shields played a significant role in medieval warfare, offering protection and symbolizing the identity of warriors on the battlefield. These shields possessed distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of shields used during that era. Let’s explore the key characteristics of wooden shields.
Material and Construction
Medieval wooden shields were primarily crafted from strong and durable wood, such as oak or pine. The choice of wood was crucial, as it needed to withstand the impact of weapons and provide sufficient defense to the warrior. The shield’s construction involved multiple layers of wood, carefully bonded together to create a sturdy and resilient structure.
To enhance their durability, wooden shields were often reinforced with metal rims or bands. These reinforcements not only strengthened the shield but also protected the edges from damage during combat. The combination of wood and metal made these shields formidable defensive tools on the battlefield.
Shape and Size
Wooden shields came in a variety of shapes and sizes, each serving a specific purpose. The shape of the shield influenced its defensive capabilities and the maneuverability of the warrior carrying it.
- Heater Shield: The heater shield, named for its resemblance to a flatiron, was one of the most popular shield designs. It featured a curved top and a pointed bottom, providing excellent protection for the torso and legs.
- Kite Shield: The kite shield, as its name suggests, had a shape reminiscent of a kite. It was longer and narrower than the heater shield, offering enhanced mobility while still safeguarding vital areas.
- Buckler Shield: The buckler shield was small and round, measuring approximately 12 to 18 inches in diameter. It was held in the hand and used for deflecting blows and parrying attacks in close combat.
- Pavise Shield: The pavise shield was large and rectangular, often used by archers and crossbowmen as portable cover during sieges or when positioned behind a fixed barrier.
Shield Decorations and Heraldry
Wooden shields were not only functional but also served as a canvas for artistic expression. Warriors often adorned their shields with decorative elements, such as intricate carvings, painted designs, or even coats of arms. These decorations not only added personal flair but also helped identify warriors on the battlefield.
Heraldry played a significant role in medieval society, and shields provided an ideal platform for displaying coats of arms, symbols, and colors associated with noble families or knights. These distinctive markings allowed warriors to showcase their identity and allegiance to a particular lord or kingdom. To learn more about medieval heraldic shields, visit our article on medieval heraldic shields.
Understanding the characteristics of wooden shields provides insight into the craftsmanship, defensive capabilities, and personal expression of warriors during medieval times. These shields were not only practical tools but also powerful symbols that represented the courage and identity of those who wielded them.
Significance of Wooden Shields in Medieval Warfare
Wooden shields played a crucial role in medieval warfare, serving various purposes that impacted the outcome of battles. Let’s explore the significance of these shields in medieval warfare, focusing on their protection and defense, symbolism and identity, and tactical use on the battlefield.
Protection and Defense
In the chaos of medieval battles, wooden shields provided vital protection to warriors on the front lines. These shields acted as a barrier against incoming projectiles, such as arrows and stones, effectively deflecting or absorbing the impact. The sturdy construction of wooden shields helped to safeguard soldiers from sword blows, providing a vital layer of defense.
Wooden shields were typically made from durable materials, such as sturdy oak or linden wood, which offered both strength and flexibility. They were often reinforced with metal rims or studs to enhance their defensive capabilities. The use of shields in close combat allowed warriors to block and parry attacks, providing them with a crucial advantage in the heat of battle.
Symbolism and Identity
Beyond their defensive functionality, wooden shields held symbolic value in medieval warfare. Shields were often adorned with distinctive designs and colors, representing the identity and allegiance of the warriors who bore them. These heraldic emblems and symbols helped to identify allies on the battlefield, fostering a sense of unity and camaraderie among comrades.
The designs on wooden shields could include family crests, coats of arms, or other personal emblems passed down through generations. By displaying these symbols, warriors showcased their lineage, honor, and loyalty to their lords or kingdoms. The intricate designs on the shields also served as a means of intimidation, instilling fear in the hearts of enemies.
Tactical Use on the Battlefield
Wooden shields were not just passive defensive tools; they also played an active role in medieval battlefield tactics. These shields were often used collectively, forming shield walls or shield formations. Warriors would lock their shields together, creating an impenetrable barrier that provided protection for themselves and their fellow soldiers.
Shield walls allowed for strategic advancements or defenses, providing cover for archers or infantry to maneuver safely. These formations were particularly effective against cavalry charges, as the tightly knit shields provided a formidable obstacle for mounted knights.
By understanding the significance of wooden shields in medieval warfare, we can appreciate their integral role in battles of the past. These shields were more than mere pieces of equipment; they were symbols of protection, identity, and strategic prowess on the battlefield. To explore different types of shields used in medieval warfare, check out our article on medieval shield types.
